Difference between revisions of "ADPNet Configuration Management"
m (minor--reformat to inline images and include header for context.) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ''Proposal and principles prepared by Tobin Cataldo in February 2016. Implemented by ADPNet [[configuration server]] management.'' | |
| − | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
=== LOCKSS In Brief === | === LOCKSS In Brief === | ||
| − | LOCKSS is a Java software appliance running well on the CentOS Linux distribution. LOCKSS nodes are typically installed and updated via RPMs on a repository maintained by LOCKSS. LOCKSS was originally designed for the preservation of e-journals and much of the functionality reflects that. While the | + | LOCKSS is a Java software appliance running well on the CentOS Linux distribution. LOCKSS nodes are typically installed and updated via RPMs on a repository maintained by LOCKSS. LOCKSS was originally designed for the preservation of e-journals and much of the functionality reflects that. While several of the LOCKSS ancillary services are specific to e-journal preservation, the core crawling, polling and repair functionality is platform and type agnostic making LOCKSS suitable for preservation in many different domains. |
* http://www.lockss.org/ | * http://www.lockss.org/ | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
=== The Impetus for Change === | === The Impetus for Change === | ||
| − | The established vendor-consumer configuration model and the discrete nature of ADPNet nodes resulted in a dependency on LOCKSS for all network-wide tasks. Finite availability left ADPNet concerns in direct competition with LOCKSS' commercial interests, which in part led to member dissatisfaction with the network. | + | The established vendor-consumer configuration model and the discrete nature of ADPNet nodes resulted in a dependency on LOCKSS for all network-wide tasks. Finite availability of LOCKSS staff time and attention left ADPNet concerns in direct competition with LOCKSS' commercial interests, which in part led to member dissatisfaction with the network. |
| + | |||
| + | The vendor-consumer configuration model employed by LOCKSS also had unintended consequences. The dependency of ADPNet members on LOCKSS support for server bring-up and configuration and software administration resulted in a reality where the ADPNet nodes were "locally outsourced" to LOCKSS. The lack of necessity in investigative and administrative control over the servers and software resulted in a lack of application specific knowledge in the network and a generalized complacency towards acquiring that knowledge. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The LOCKSS preservation network is designed to be node-independent. With distributed, potentially heterogeneous, hardware containing full copies of data and operating independently in the network, there is no node that supersedes or has a greater magnitude of precedence than the other network nodes. The same assertion cannot be made for the vendor-consumer configuration model with a centralized service passing configuration values and a dependency on LOCKSS support. The disruption of that link with LOCKSS would significantly impair ADPNet's ability to offer continuous service. Any new configuration management model should be network driven, node-independent, and the onus put squarely on ADPNet membership. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Configuration Server == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === The Vendor-Consumer Administrative Model === | ||
| + | |||
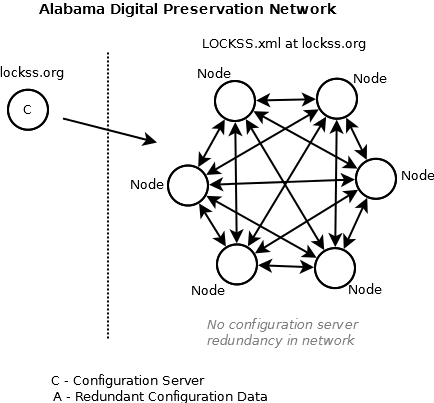
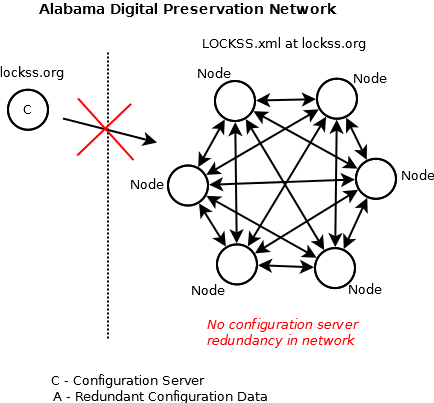
| + | The vendor-consumer administrative model is hierarchical in nature and lacks redundancy within the preservation network. Without software services infrastructure and current configuration data redundancy within the preservation network, the vendor-consumer administrative model creates a network dependency that is not fault tolerant and is ultimately a vulnerability to the preservation network. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[:File:Adpnet-configuration-management-currentnetwork.png|ADPNet in the vendor-consumer administrative model]] : | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Adpnet-configuration-management-currentnetwork.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[:File:Adpnet-configuration-management-currentnetworka.png|A disruption in the network]] : | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Adpnet-configuration-management-currentnetworka.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Node-based Configuration Management === | ||
| + | |||
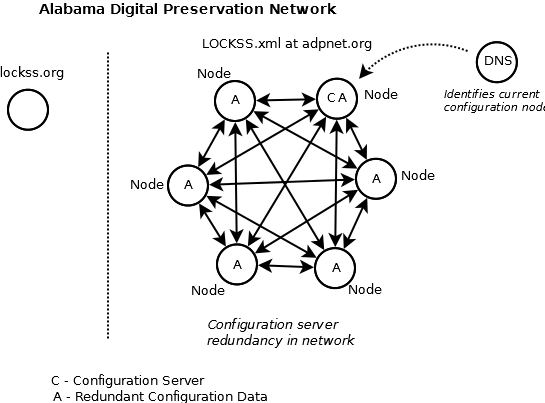
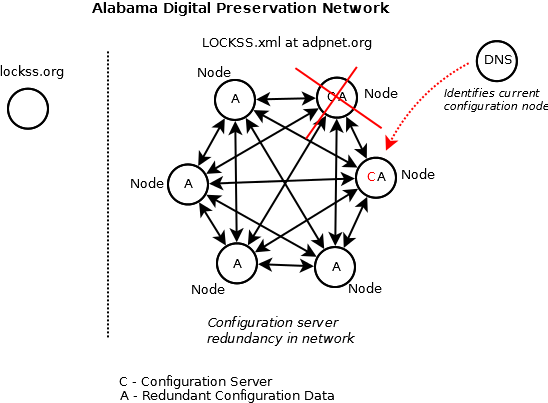
| + | The node-based configuration management model looks to establish a fully replicable configuration services provider infrastructure that can be brought up by any network member. In order for the configuration services infrastructure to be fully reproducible, it should not be dependent on hardware infrastructure that is not common to every network member. The only common hardware infrastructure that is common to every (host) member is the preservation node. In the node-based configuration management model, a preservation node is promoted to configuration services provider for the network. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to create a model that can seamlessly transfer configuration services from one preservation node to another, a persistent URL should be utilized. ADPNet is utilizing a host answer record for the common domain. The A record identifies the static IP for the promoted preservation node. Node promotion can be transferred by indicating a new IP endpoint in the A record. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The promoted node exposes the configuration data and backend sources for the configuration services infrastructure through URLs (starting with the persistent URL). ADPNet has created an archival unit that targets the exposed data. The base URL is the persistent URL. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[:File:Adpnet-configuration-management-Proposednetwork1.png|ADPNet in the node-based configuration management model]] : | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Adpnet-configuration-management-Proposednetwork1.png]] | ||
| − | + | [[:File:Adpnet-configuration-management-proposednetwork1a.png|A disruption in the network]] : | |
| − | + | [[Image:Adpnet-configuration-management-proposednetwork1a.png]] | |
Latest revision as of 13:40, 3 July 2019
Proposal and principles prepared by Tobin Cataldo in February 2016. Implemented by ADPNet configuration server management.
Overview
This document describes the configuration management model for ADPNet. The configuration management model should be understood in the larger context of the purpose of ADPNet and the LOCKSS software functional design.
ADPNet In Brief
ADPNet is a collaborative agreement of various Alabama institutions to implement and maintain a distributed digital preservation network. In the original implementation, ADPNet members borrowed heavily from the MetaArchive model of re-purposing LOCKSS for general preservation use.
LOCKSS In Brief
LOCKSS is a Java software appliance running well on the CentOS Linux distribution. LOCKSS nodes are typically installed and updated via RPMs on a repository maintained by LOCKSS. LOCKSS was originally designed for the preservation of e-journals and much of the functionality reflects that. While several of the LOCKSS ancillary services are specific to e-journal preservation, the core crawling, polling and repair functionality is platform and type agnostic making LOCKSS suitable for preservation in many different domains.
- http://www.lockss.org/
- http://documents.clockss.org/index.php/LOCKSS:_Basic_Concepts
- https://github.com/lockss/lockss-daemon
ADPNet Historic Configuration Model
While founding members of ADPNet had experience with LOCKSS through MetaArchive, functional experience did not extend to the depth of knowledge requisite to build and run and preservation network. As a result, LOCKSS was enlisted to provide administrative and technical support. The resulting configuration management model mimicked the commercial GLN and CLOCKSS hierarchical vendor-consumer support topology; a LOCKSS-controlled configuration server passed directives to the ADPNet preservation nodes. While ADPNet members have local administrative control over the preservation node, the shared configuration files, necessary for proper network communications, were controlled by LOCKSS.
The Impetus for Change
The established vendor-consumer configuration model and the discrete nature of ADPNet nodes resulted in a dependency on LOCKSS for all network-wide tasks. Finite availability of LOCKSS staff time and attention left ADPNet concerns in direct competition with LOCKSS' commercial interests, which in part led to member dissatisfaction with the network.
The vendor-consumer configuration model employed by LOCKSS also had unintended consequences. The dependency of ADPNet members on LOCKSS support for server bring-up and configuration and software administration resulted in a reality where the ADPNet nodes were "locally outsourced" to LOCKSS. The lack of necessity in investigative and administrative control over the servers and software resulted in a lack of application specific knowledge in the network and a generalized complacency towards acquiring that knowledge.
The LOCKSS preservation network is designed to be node-independent. With distributed, potentially heterogeneous, hardware containing full copies of data and operating independently in the network, there is no node that supersedes or has a greater magnitude of precedence than the other network nodes. The same assertion cannot be made for the vendor-consumer configuration model with a centralized service passing configuration values and a dependency on LOCKSS support. The disruption of that link with LOCKSS would significantly impair ADPNet's ability to offer continuous service. Any new configuration management model should be network driven, node-independent, and the onus put squarely on ADPNet membership.
Configuration Server
The Vendor-Consumer Administrative Model
The vendor-consumer administrative model is hierarchical in nature and lacks redundancy within the preservation network. Without software services infrastructure and current configuration data redundancy within the preservation network, the vendor-consumer administrative model creates a network dependency that is not fault tolerant and is ultimately a vulnerability to the preservation network.
ADPNet in the vendor-consumer administrative model :
Node-based Configuration Management
The node-based configuration management model looks to establish a fully replicable configuration services provider infrastructure that can be brought up by any network member. In order for the configuration services infrastructure to be fully reproducible, it should not be dependent on hardware infrastructure that is not common to every network member. The only common hardware infrastructure that is common to every (host) member is the preservation node. In the node-based configuration management model, a preservation node is promoted to configuration services provider for the network.
In order to create a model that can seamlessly transfer configuration services from one preservation node to another, a persistent URL should be utilized. ADPNet is utilizing a host answer record for the common domain. The A record identifies the static IP for the promoted preservation node. Node promotion can be transferred by indicating a new IP endpoint in the A record.
The promoted node exposes the configuration data and backend sources for the configuration services infrastructure through URLs (starting with the persistent URL). ADPNet has created an archival unit that targets the exposed data. The base URL is the persistent URL.